|
www.HealthyHearing.com |
Tinnitus in one earWhy it happens and what to do about it
Contributed by Emily Ostrowski, content manager, Healthy Hearing Key points:
Tinnitus is the medical name for ringing in the ears, a common symptom often connected to hearing loss and noise damage. It may sound like a buzzing, humming, hissing or other noise. It may come and go, or become chronic. It's also very common. Between 10-25% of adults have tinnitus, according to the National Institution on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD). In most cases, tinnitus affects hearing in both ears. More rarely, it sometimes affects just one ear, known as unilateral tinnitus. Treatment will depend on what's causing the tinnitus. For some people, correct diagnosis and treatment may make it go away completely. Others may need to learn how to manage it as a chronic condition, especially if it's linked to hearing loss, which is permanent. Is it normal to have tinnitus in one ear?In short, yes. While experiencing tinnitus in one ear is more rare, it isn't inherently more worrisome, experts note. "Tinnitus is both ears is more common, although it is not unusual for the tinnitus in one ear to be louder than the other," said Dr. Allison King, AuD, an audiologist at Palmetto Family Hearing Center in Waxhaw, NC. Uneven tinnitus (louder in one ear) is known as asymmetric tinnitus. A large 2025 study of veterans found that about 54% experienced tinnitus bilaterally (in both ears), 35% asymmetrically and 11% unilaterally.
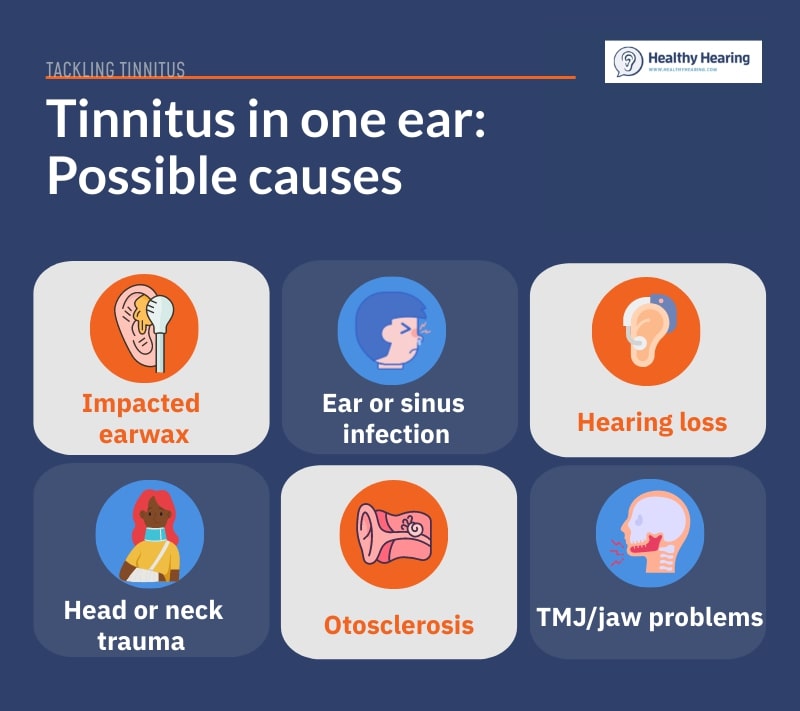
Unilateral tinnitus causes and treatmentsWhen tinnitus is one-sided, it's more likely to be caused by one of the following conditions: One-sided hearing lossHearing loss often leads to tinnitus. When it affects only ear ear, it is known as unilateral hearing loss (or singled-sided deafness if severe). Some people are born with the condition, while others develop it later in life. Treatments may include:
Acoustic neuromasAcoustic neuromas, also referred to as vestibular schwannomas, are rare, benign tumors found on the vestibulocochlear nerve. This nerve is responsible for hearing and balance. In addition to ringing in one ear, an acoustic neuroma may cause dizziness, hearing problems in the affected ear and problems with coordination. Acoustic neuromas are monitored if small and not problematic. Surgery or radiation therapy is recommended for larger tumors or those causing a lot of symptoms. Earwax buildupEarwax buildup or impaction happens when your ear produces too much earwax, or earwax is getting stuck. When this happens, a person may experience hearing problems, tinnitus, and itchiness or discomfort. Earwax blockage should be treated having a professional earwax removal. Trying to do it on your own may make the impaction worse or even damage your eardrum. Middle ear infectionA middle ear infection is an infection behind the eardrum. Swelling and inflammation causes pain (earaches), muffled hearing and sometimes a fever. While middle ear infections can go away on their own, they are often treated with antibiotics to prevent complications. If you or your child have a suspected ear infection, see a doctor. OtosclerosisOtosclerosis is abnormal bone growth in the middle ear. It is a rare condition that can lead to progressive hearing loss as the bone growths get worse. In the mild stages, it can be treated with hearing aids. In more severe cases, a doctor may recommend a surgery known as stapedectomy. Injuries or traumaInjuries to one ear or the side of the face, such as a bad fall, can lead to tinnitus. This is because the injury damages the delicate structures of the ear or the nerves involved in hearing. Depending on the injury, physical therapy or surgical procedures may help to heal your body. As the injury heals, the tinnitus will most likely go away. Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disordersTMJ refers to a condition affecting the joint that connects your lower jaw to your skull. This joint can become strained, and cause pain, stiffness, and dysfunction. (Some people can audibly "pop" their TMJ joint). This disorder can lead to one-sided tinnitus due to pressure or nerve irritation caused by jaw misalignment or muscle tension. TMJ is often treated with a combination of jaw realignment therapy, physical therapy, night guards and anti-inflammatory medication. Things to keep in mindThe conditions listed above are some of the more common triggers of tinnitus in one ear, but not all of them. Also, while you may feel like your tinnitus is only in one ear, you may actually be experiencing it in both ears, and just not realizing it. "Tinnitus is cortical—it [originates] in the brain, even though it is perceived in the ears," said Dr. King. "So often times, what is perceived as sound in one ear, is really present in both but just more noticeable in one than the other." When is one-sided tinnitus an emergency?Most of the time, unilateral tinnitus isn't a sign of an emergency. However, there are instances where it warrants prompt medical attention. "Tinnitus that is sudden and does not stop should be evaluated by a medical doctor, preferably an ENT physician, as soon as possible. This is especially true if it is accompanied by hearing loss or dizziness," said Dr. King. Sudden hearing loss that occurs out of the blue or rapidly over the course of a few days needs to be evaluated by a medical professional right away. Sudden hearing loss is an emergency that needs to be treated right away to help rule out life-threatening causes (such as a stroke) and to prevent any hearing damage from becoming permanent. Additionally, if you regularly hear whooshing or the thumping of your heartbeat in your ear, you may have what's called pulsatile tinnitus. This could indicate a problem with your blood vessels or high blood pressure, and should be checked out by a medical professional as soon as possible. The link between hearing loss and tinnitusTinnitus and hearing loss often go hand in hand. According to the American Tinnitus Association (ATA), research suggests that "approximately 90% of tinnitus patients have some degree of hearing loss." Hearing loss often comes on gradually, and the signs can be so subtle at first that they can be easy to miss. If you've noticed difficulty hearing in places with a lot of background or struggle to follow some conversations, it may be a good idea to get your hearing checked. Will hearing aids help?Yes. Hearing aids can provide relief for many people with both unilateral and bilateral tinnitus. Hearing aids amplify external sounds, making the ringing or buzzing in your ears less noticeable. Many modern hearing aids also come with tinnitus masking features, such as white noise or sound therapy, to further reduce the perception of sound. Learn more: How hearing aids help tinnitus Should you wear one hearing aid or two?You might assume that if you only perceive ringing or buzzing in one ear, that you only need to use one hearing aid. However, except for very specific situations, two hearing aids are better than one. "When a hearing loss is diagnosed, it is important to treat the hearing loss with amplification in both of the ears where the hearing loss is present, regardless of where the tinnitus is perceived," said Dr. King. What to do if no cause is foundThere are many cases where you may not be able to identify a direct cause for your one-sided tinnitus. In that case, management is the same for one ear as it would be for two, and can include strategies such as:
Learn more: Tinnitus treatments If you are experiencing tinnitus that is impacting your quality of life and causing you distress, visit your medical provider to see if they can determine a cause or recommend next steps. It's also a good idea to find a hearing professional near you to help manage your symptoms. A hearing specialist will discuss your symptoms, medical history, and any potential noise exposure. They will likely perform a comprehensive hearing test to look for hearing loss and conduct additional tests to check for any underlying ear conditions. They may also use pitch-matching or loudness tests to better understand how your tinnitus is perceived and come up with effective treatment options. Emily Ostrowski, content manager, Healthy Hearing
|
Featured clinics near me
Earzlink Hearing Care - Reynoldsburg
7668 Slate Ridge Blvd
Reynoldsburg, OH 43068

Find a clinic
We have more hearing clinic reviews than any other site!



 Emily is an experienced journalist and medical content writer based in Maine. Passionate about delivering enlightening and accurate content, she is committed to empowering people to make informed choices regarding their hearing health.
Emily is an experienced journalist and medical content writer based in Maine. Passionate about delivering enlightening and accurate content, she is committed to empowering people to make informed choices regarding their hearing health.