|
www.HealthyHearing.com |
Hearing aid batteries
By Joy Victory, managing editor, Healthy Hearing  Reviewed by
Megan Gerhart, audiologist Reviewed by
Megan Gerhart, audiologist Last updated on: January 30th, 2026 Hearing aid batteries power your devices. Rechargeable hearing aids are increasingly popular, but in some cases, replaceable "button" batteries are still used. Key points:
Like most modern technology, hearing aids rely on batteries to function. Traditionally, hearing aids used tiny "button" batteries that wearers had to replace every few days to weeks. Now, though, many hearing aids come with rechargeable batteries. When choosing a hearing aid, it's a good idea to think through which battery type works best for you. What to know about rechargeable hearing aid batteries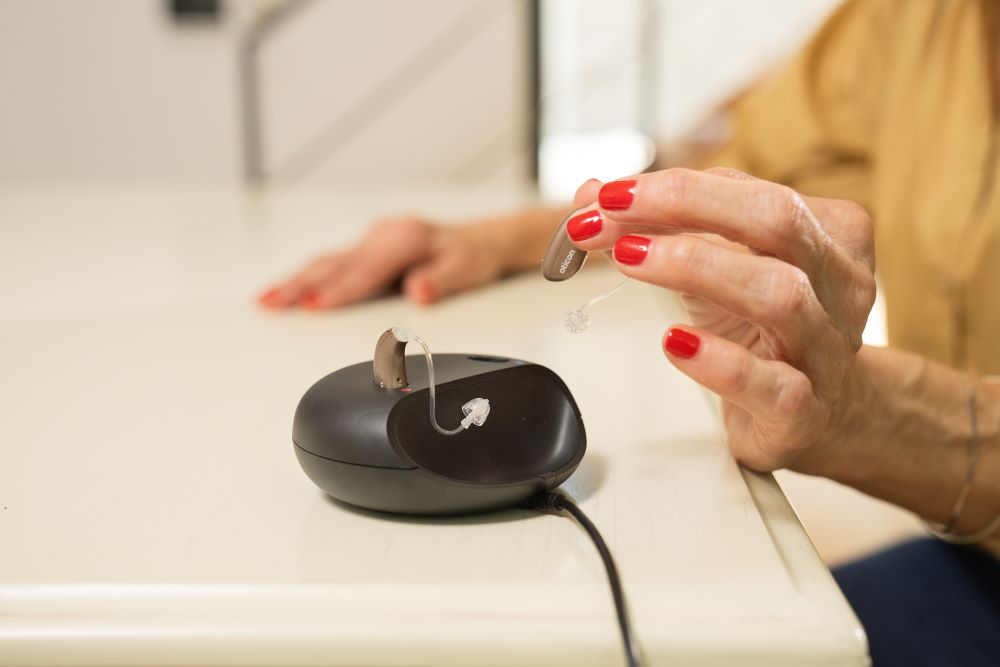
overnight. Many modern hearing aid models come with rechargeable lithium-ion batteries. These batteries are usually recharged at night, when you take out your hearing aids to sleep. They are available in both behind-the-ear and in-the-ear models. How do rechargeable hearing aids work?Rechargeable hearing aids work a lot like smartphones—you need to charge them regularly to keep them working. Most come with a simple docking station. At night, just take out your devices, place them in the charger and go to bed. By morning, they’ll be ready for a full day of use. How long do rechargeable hearing aid batteries last?Rechargeable batteries are designed to last a full day, typically providing 16–30 hours of use per charge. However daily battery life will vary based on factors like:
How do you charge them?Gently remove your hearing aids, clean them, and place them in the designated (left or right) docking stations. Left ears are typically marked blue, and right ears are marked red. Most chargers will have flashing lights indicating they are charging, while a solid light means they are charged. In newer hearing aid models, you do not need to turn them off prior to placing them in the charger. What if you forget to recharge your battery?The main downside to rechargeable batteries is that if you forget to charge them (or lose your charger) they won't work. Some rechargeable hearing aids allow for a quick partial charge that can still provide meaningful use for most of your day. For example, Oticon Zeal™ allows you to charge your device for just 30 minutes to get up to eight hours of battery life.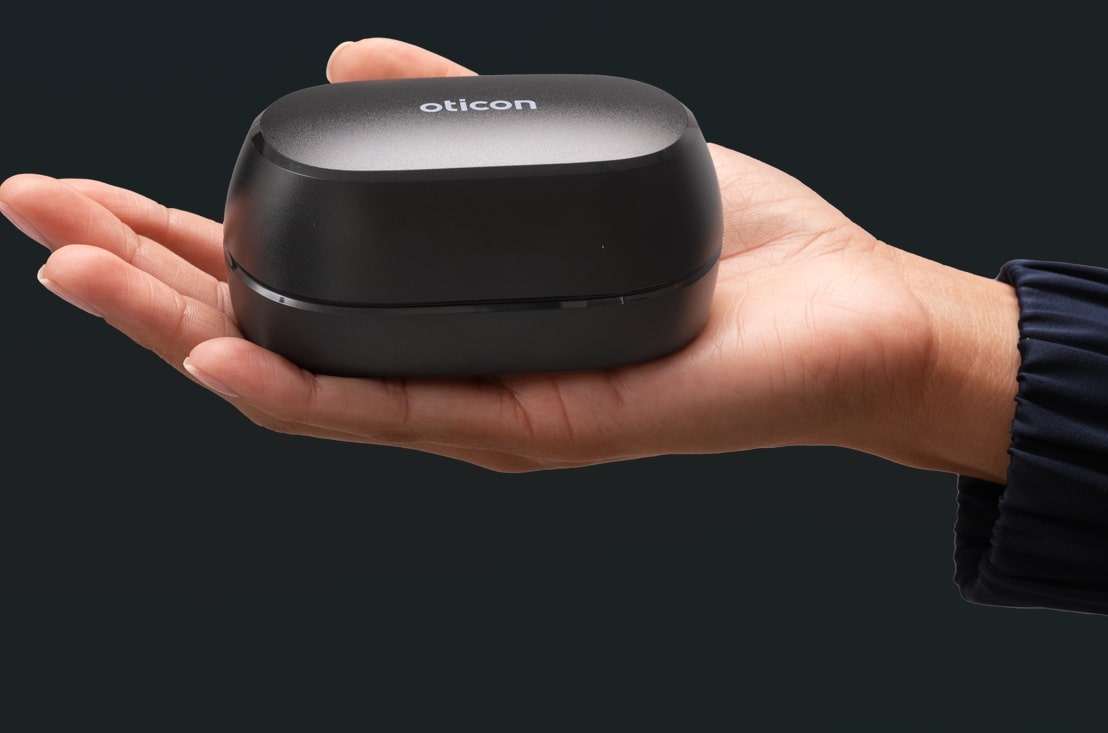 
Additionally, newer models may come with wireless, portable chargers that you can bring with you as you go about your day, making sure your hearing aid never runs out of power. When do rechargeable hearing aid batteries need to be replaced?Most rechargeable batteries last three to five years before needing to be replaced. If you start to notice that you can't get a full day's use from your battery even after a full night of charging, this may be a sign it's time for replacement. Popular rechargeable hearing aidsRechargeable hearing aid brands on the market from manufacturers in 2026 include:
Please note other manufacturers also may offer rechargeable hearing aids; these are some of the top-sellers. More: Pros and cons of hearing aids with rechargeable batteries What to know about disposable hearing aid batteries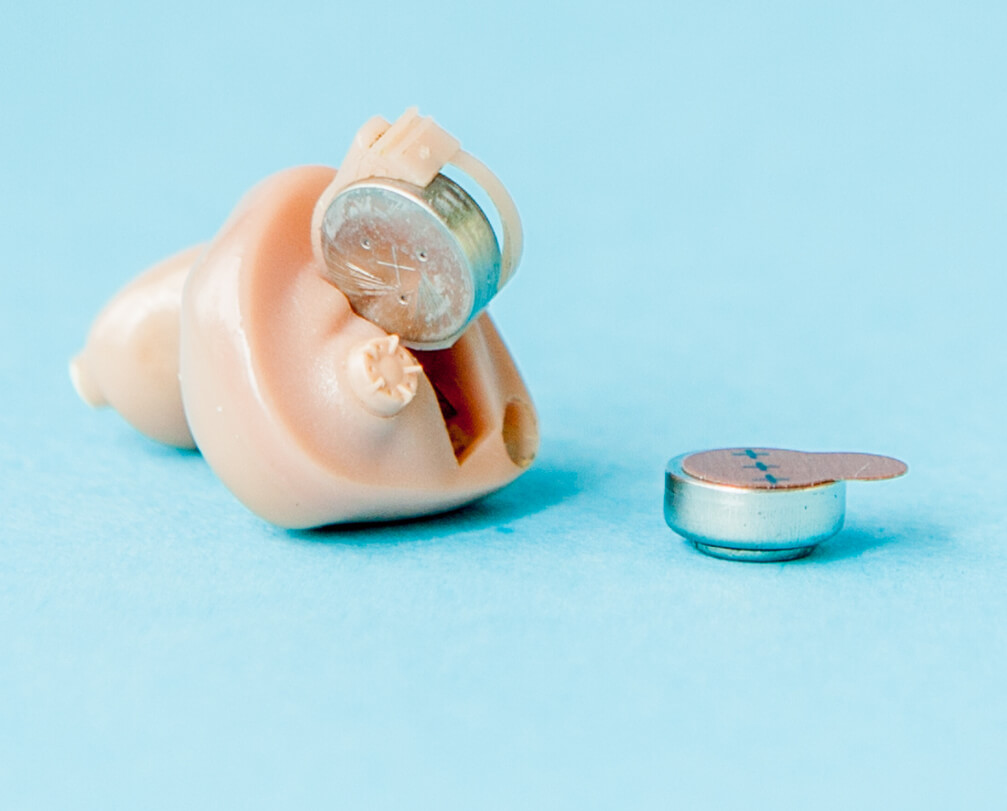
becoming far less common. Before rechargeable hearing aids became common, all devices used disposable zinc-air “button” batteries. Today, they’re most often found in power hearing aids for severe or profound hearing loss, since those devices need more energy. Additionally, most custom hearing aids continue to use disposable batteries, and many companies still make non-rechargeable versions of their devices for patients who prefer them. Zinc-air batteries are air-activated. A small sticker keeps them inactive until it’s removed. Once you peel it off, oxygen enters the battery and turns it on. For best performance, wait about one minute after removing the sticker before inserting the battery. Replacing the sticker will not deactivate the battery, so once the sticker is removed, the battery will remain in an active state until the power runs out. What are the different sizes of disposable hearing aid batteries?Hearing aids come in many different sizes and styles and with different power needs. Larger hearing aids require larger batteries. There are four sizes of hearing aid button batteries available on the market. The sizes from smallest to largest are: 10, 312, 13 and 675. Hearing aid batteries are all smaller than the diameter of a dime:
Color-coding for disposable hearing aid batteriesBecause size differences may be hard to notice and difficult to remember, battery packaging is color-coded so finding and purchasing the correct ones is easier.
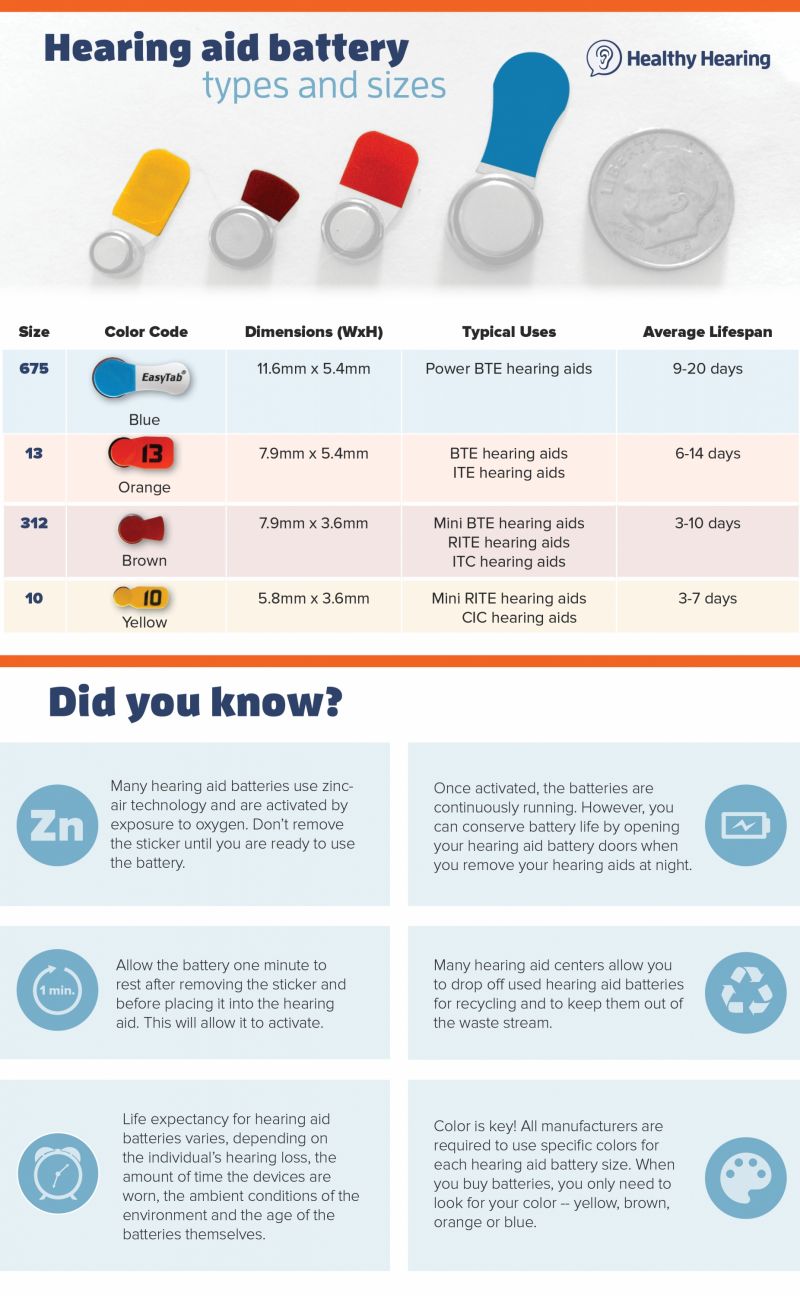 (Key: BTE=behind the ear, ITE=in the ear, RITE=receiver in the ear; ITC=in the canal; CIC=completely in the canal.) How long do standard hearing hearing aid batteries last?Non-rechargeable hearing aid batteries can last anywhere from five to 14 days, based on a 16-hour day of wear. This depends on the size of the battery and power needed by the hearing aid. Typically, smaller batteries have shorter battery life than larger ones. The average lifespan of hearing aid batteries is as follows:
Can I make my hearing aid battery last longer?Not exactly, but you can take steps to ensure the power isn’t being wasted, including:
If you are experiencing shortened battery life, there may be an issue with the hearing device. In this case, you should consult your user manual or contact your hearing healthcare professional to make sure everything is working properly. More: How to get the most from your hearing aid batteries Popular hearing aid battery brandsCommon manufacturers of non-rechargeable hearing aid batteries include Rayovac and Energizer. However, many hearing aid manufacturers sell batteries wholesale to hearing care professionals, and the batteries may carry the brand name of that hearing aid manufacturer. Another common practice is private labeling of batteries. This means the hearing care professional may purchase batteries wholesale and have them labeled with the name, address, phone number and logo associated with their office. Regardless of the branding, most hearing aid batteries are made by trusted companies that produce other types of batteries for all types of electronics. Where to purchase hearing aid batteriesBatteries are available in a variety of different locations, including:
Getting batteries from your hearing specialistYou might also choose to purchase batteries through your hearing specialist. Because hearing care providers go through their stock of batteries quickly, many wearers feel they are getting fresher batteries. Also, if you forget what battery size you need for your particular device, the hearing healthcare professional will ensure you are purchasing the correct one. Additionally, it’s worth asking if your hearing health practitioner offers any kind of battery club or discount program. These programs can save you money on your battery purchases and, in some cases, you can request the batteries be sent directly to you saving you a trip to the office. A note on hearing aid battery safetyIf you have disposable batteries, make sure to keep them in a safe place where children and pets can't reach them. According to the National Capital Poison Center, more than 3,500 Americans of all ages swallow disposable button batteries every year. If this happens to a person or pet in your home, seek medical attention immediately. More: Hearing aid battery safety and disposal The Bluetooth® word mark and logos are registered trademarks owned by Bluetooth SIG, Inc. The Auracast™ word mark and logos are trademarks owned by the Bluetooth SIG. Any use of such marks by Demant is under license. Other trademarks and trade names are those of their respective owners.Joy Victory, managing editor, Healthy Hearing
You are reading about: Related topics
More information about hearing loss, hearing aid brands, assistive devices and tinnitus. Featured clinics near me
Earzlink Hearing Care - Reynoldsburg Find a clinicNeed a hearing test but not sure which clinic to choose? Call 1-877-872-7165 for help setting up a hearing test appointment. Related contentThe Healthy Hearing Report |
|
www.HealthyHearing.com |
Hearing aid batteries
By Joy Victory, managing editor, Healthy Hearing  Reviewed by
Megan Gerhart, audiologist Reviewed by
Megan Gerhart, audiologist Last updated on: January 30th, 2026 Hearing aid batteries power your devices. Rechargeable hearing aids are increasingly popular, but in some cases, replaceable "button" batteries are still used. |


 Joy Victory has extensive experience editing consumer health information. Her training in particular has focused on how to best communicate evidence-based medical guidelines and clinical trial results to the public. She strives to make health content accurate, accessible and engaging to the public.
Joy Victory has extensive experience editing consumer health information. Her training in particular has focused on how to best communicate evidence-based medical guidelines and clinical trial results to the public. She strives to make health content accurate, accessible and engaging to the public.